- Home >
- Electro >
- Raspberry Pi > Kitronik Robotics Board For Raspberry Pi Pico
Kitronik Robotics Board For Raspberry Pi Pico
With Kitronik's compact robotics board for Raspberry Pi Pico, you can make the Raspberry Pi Pico the heart of your new robotics project.
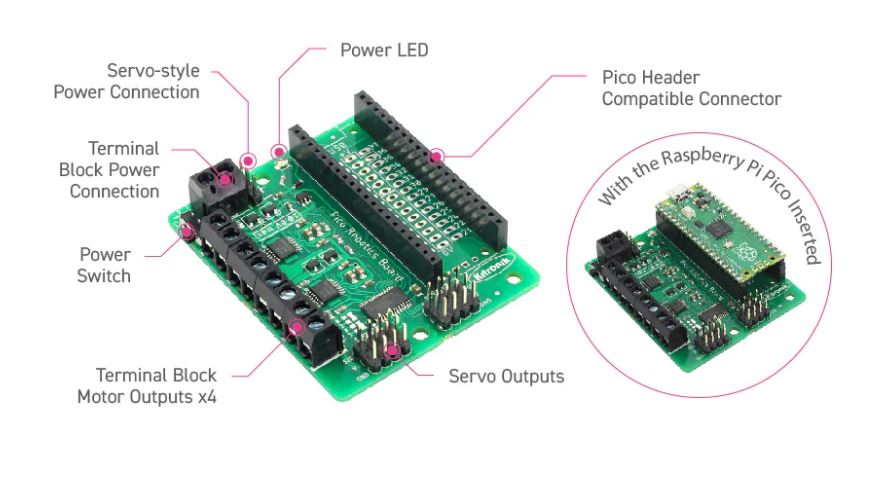
The Raspberry Pi Pico (connected via a connector) can run 4 motors (or 2 stepper motors) and 8 servos with this compact robotics board. It also has 27 additional I/O expansion ports, as well as power and ground connectors.
Kitronik robotics board for Raspberry Pi Pico
With Kitronik's compact robotics board for Raspberry Pi Pico, you can make the Raspberry Pi Pico the heart of your new robotics project. The Raspberry Pi Pico (connected via a connector) can run 4 motors (or 2 stepper motors) and 8 servos with this compact robotics board. It also has 27 additional I/O expansion ports, as well as power and ground connectors.
Two dual H-bridge motor driver ICs are included on the robotic board. They can each drive two conventional motors or one stepper motor, with full forward, reverse and stop control. In addition, there are eight servo outputs, which can drive stepless or continuous servos. The Pico can control them all using the I2C interface and a 16-channel driver IC. The IO output connects to any unused pins on the Pico. Other devices, such as sensors or ZIP LEDs, can be added to the board using the 27 available I/O pins.
Power is supplied via a terminal block or servo connection. Power is then controlled by an on/off switch on the board, and a green LED indicates that the board is powered up. The board then generates a regulated 3.3V supply which is fed into the 3V and GND connectors to power the Pico. There is therefore no need to power the Pico independently. The 3V and GND pins are also separate on the connector, allowing power to be supplied to other devices.
To use the robotics board, insert the Pico firmly into the two-row pin connector on the board. Assemble the Pico by placing the USB connection at the same end as the power connectors on the robotic board. This will give you access to all the features of the board and to each pin that has been disconnected.
- A small, feature-rich board designed to power your Raspberry Pi Pico robotics projects.
- The board can power four motors (or two stepper motors) with full forward, reverse and stop control, as well as eight servos.
- It also has 27 additional I/O expansion ports, as well as power and ground connectors.
- The I2C communication channels are also separate, allowing control of other I2C compatible devices.
- The board also has an on/off switch and a power status LED.
- The board is powered by a terminal block or servo connection.
- External devices can be powered by separating the 3V and GND pins of the solder pads.
- Code it in MicroPython using an editor such as the Thonny editor.
- Raspberry Pi Pico board not included.
Robotics board for Raspberry Pi Pico: content, requirements and resources
Contents :
- 1 x Kitronik Compact Robotics Board for Raspberry Pi Pico.
Prerequisite:
- A Raspberry Pi Pico board.
Resources :
- Example MicroPython class and sample code - GitHub repository.
- Example CircuitPython class and sample code - GitHub repository.
- Get started with MicroPython on Raspberry Pi Pico.
- Tech Talks - live stream playback.
- Raspberry Pi Pico frequently asked questions.
- More information on the Pico.
- About MicroPython.
- About Python.
- The Thonny editor.
- Raspberry Pi Pico Datasheet.
- RP2040 Datasheet.
Contents :
- 1 x Kitronik Compact Robotics Board for Raspberry Pi Pico.
Prerequisite:
- A Raspberry Pi Pico board.